|
MOSKVORECHYE ENVIRONMENT RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINATION
COMPLEX INVESTIGATION AND ESTIMATION CAUSED BY MEPHI IRT (STANDARD
RESEARCH REACTOR)-2000 REACTOR LONG-DURATION USE.
INTRODUCTION
Today in Moscow region there is
a long-lived diffuse technogenic radioactive contamination mainly
caused by 1986 Chernobyl accident and nuclear weapon tests products.
Russian nuclear power industry emission influence on this contamination
forming is ignorable.
"Moskvorechye-Saburovo" municipal
district (South administrative district of Moscow) characteristic
property is extra environment radioactive contamination caused
by set of factories. Here we mean standard or emergency factory
work environment contamination. We have not considered environment
contamination caused by radioactive materials loss or thefts.
MEPhI IRT-2000 reactor (standard
research reactor) was started in the end of 1967 placed on Moscow
Engineering Physics Institute territory and is the safest in that
type nuclear-technical installation. In more than 30 years use
there has not been an emergency accompanied with an extra radioactive
products environment emission. Nevertheless MEPhI IRT-2000 reactor
is formally classified as nuclear-dangerous object and surrounding
territories extra radioactive contamination caused by its (reactors`s)
long-duration use was able to form.
In region there are some factories
(except MEPhI) and their work is able to cause marked environment
radioactive contamination. So the conclusion about pollution origin
(caused it by IRT-2000 reactor use or other factories) can be
made using technogenic radionuclides environment content and distribution
detailed information.
1. Sampling objects and measurement technique.
For radionuclides (MEPhI IRT-2000
reactor long-duration use products) Moskvorechye environment surface
ecosystems elements ingress and accumulation estimation the following
samples selection on above-mentioned territory were executed:
surface ground layer with depth up to 2 cm, surface ground layer
with vegetation rest in (grass root, moss) and fallen leaves and
branches (if they were) with depth up to 2 cm, layer-by-layer
ground samples with depth up to 30 cm (one layer depth is between
1 and 3 cm).
For estimation of atmospheric
radionuclides receipt influence on studied territory litter contamination
snow cover and annual grass vegetation samples selection was executed.
Planning and sampling operative
correction with regard to measurement results were executed using
"Moskvorechye" GIS developed in our Laboratory. Ground and vegetation
sampling was executed after complete snow cover melting. To increase
sampling sensitivity sample collection was executed in natural
concentrators (if it was possible) such as hollow, narrow gully
etc. Other territory sampling frequency was more rare and sampling
places choice was executed in much the same way.
Similar environment objects samples
were collected at 50 Moscow and vicinity auditorial locations
placed far enough from IRT-2000 reactor, that is off its influence
zone. The same sampling places choice techniques and sampling
itself were used. These samples analysis technique was the same
and the same radionuclide set content was measured as the samples
chosen at Moskvorechye territory.
In this research for studied region
environment objects technogenic and natural gamma-radiation radionuclides
content information receipt HPGe low-background gamma-spectrometry
technique was used. It was necessary to measure more than 400
samples technogenic 137Cs, 134Cs, 60Co,
54Mn and other radionuclides specific activity at a
level of ~0.05-0.1Bk/(sample kg) with this sample natural 226Ra
and 232Th radionuclide activity at a level of 10-40
Bk/kg and 40K at a level of 100-600 Bk/kg.
Snow sample 3T content
measurement was executed using liquid scintillation spectrometry.
 |
 |
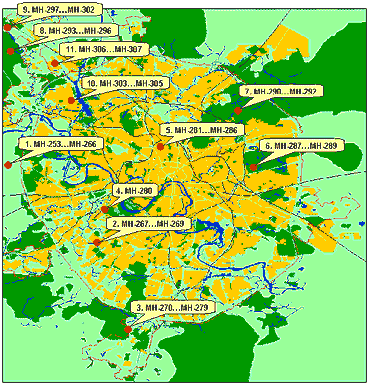
Auditorial sampling points in Moscow and vicinity. |
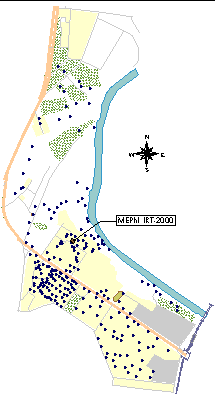
Sampling points in Moskvorechye district. |
|