|
Experimental results.
The airborne gamma-spectrometry methods and devices designed were successfully used for the investigation
of the USSR European territory Chernobyl accident contamination in 28 April - 26 September 1986 period.
The radioactive contamination of the territories of Semipalatinsk Test Site (1989-1990) and
Novaja Zemlja Islands South part (1995) after nuclear tests stop were also investigated by the
MEPhI specialists by means of the methods and devices designed.
In June-July 2003 the airborne survey of some territories of Moscow region was conducted by MEPhI
and "Radon" specialists collaboration. The "Radon" Ka-26 helicopter was equipped with MEPhI AGSS-99S
for this purpose. The flights over territories of interest were organized by regular parallel tacking
(200-400 meters from each other) at 100 meters height and 30 m/sec velocity. The coordinate information
was GPS based and by MEPhI methods corrected for better gamma-emitting sources localization and
identification.
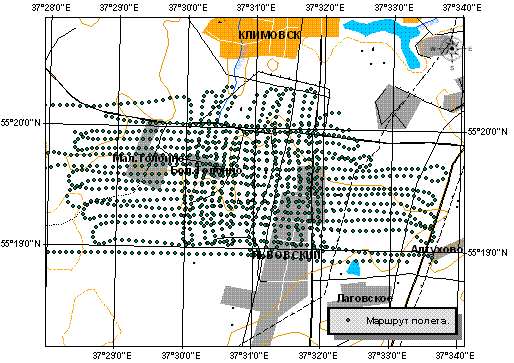
Survey plan.
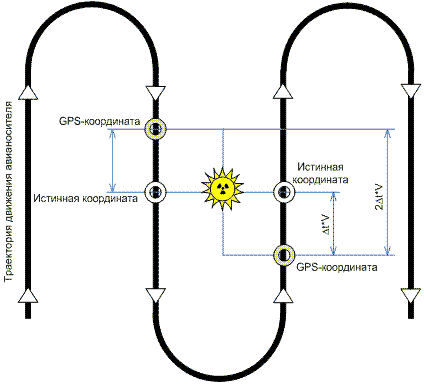
GPS time-lag effect on positioning accuracy during parallel tacking
(here Dt – GPS data output interval,
V – average aircraft velocity).
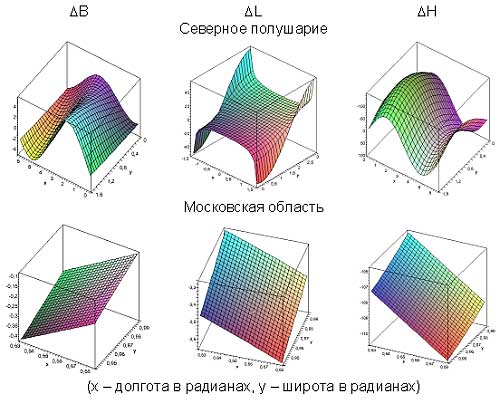
Longitude (DB), latitude (DL)
and altitude (DH) correction switching from WGS-84 to Pulkovo-42 datum.
The airborne data were processed by MEPhI designed software and programs. The spatial distributions and
the corresponding maps for point source localization criterion NSI (Normalized Spectral Index) and
137Cs, 40K, 226Ra, 232Th were constructed.
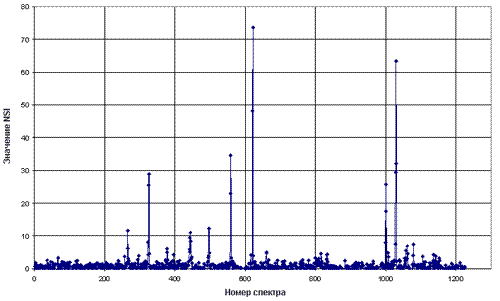
NSI distribution along the flight trajectory.
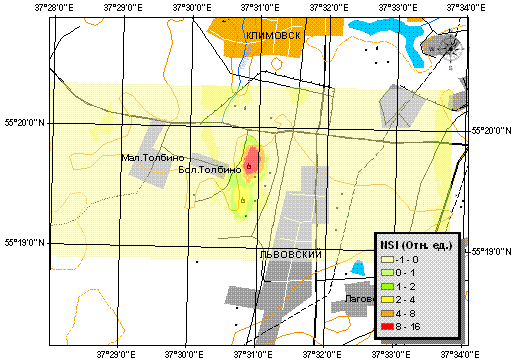
NSI distribution on territory surveyed.
To calculate the artificial or natural nuclide activity (concentration) we have developed the "peak"
method for airborne spectra processing. The essence of the method is the full energy absorption peak count
rate and its total uncertainty correct calculation.
In case the spectra is obtained in AGSS measurements the full energy absorption peak count rate correct
calculation appears to be a problem because of the scintillation detector poor energy resolution, short
measuring time (that is poor statistics) and a great amount of continuum in spectra due to the air scatted
radiation. To overcome this problem we have developed the "resolution improvement" method that enables
to calculate accurately the full energy absorption peak count rate and its total uncertainty in the airborne
spectra for the energy range 150-3000 keV. The essence of the method is a number of transformations of the
measured spectrum resulting in peak width critically (2-3 times) decrease.
The results of these methods application are displayed for three different gamma-emitting source types.
The measured and the transformed spectra are presented for A, B, C gamma-emitting source type.
Place mouse cursor on picture to see the results of processing.
A - the flight over the 137Cs significantly contaminated territory and the 40K, 226Ra and 232Th normal concentration;
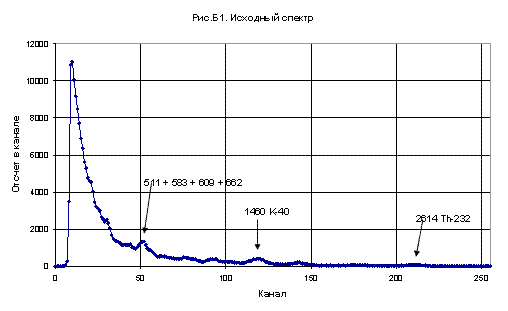
B - the flight over the 137Cs slightly contaminated territory and the 40K, 226Ra and 232Th normal concentration;
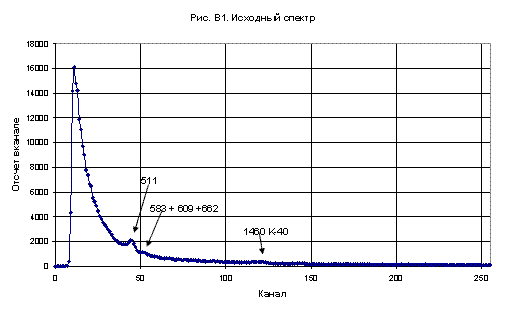
C - the flight over the operating nuclear reactor, producing the 16N high air
concentration; the 16N decay is accompanied by high energy gamma-radiation emission producing
a very strong annihilation peak in this spectra type.
The rather strong 137Cs local contamination was discovered near town of Podolsk (Moscow visinity).
The concentration maximums were localized and identified. One can see from the 137Cs contamination
map presented that two contaminated maximums register with two plant positions.
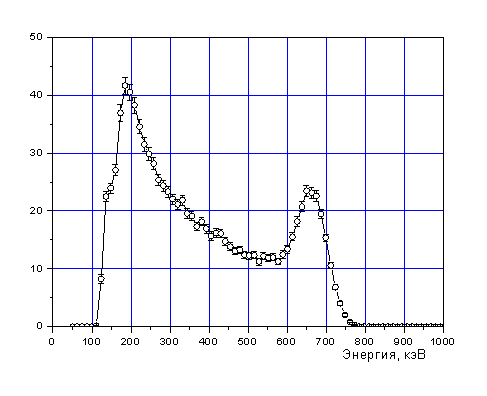
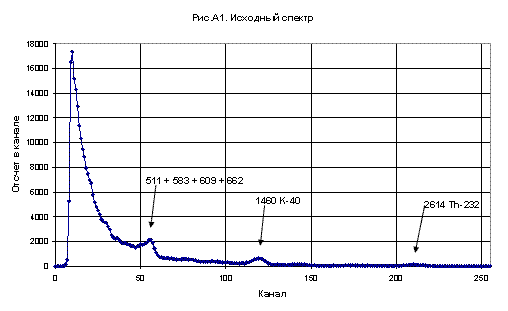
Found radioactive source spectrum.
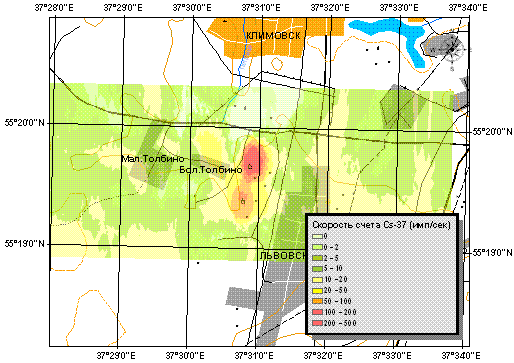
Cs-137 count rate distribution.
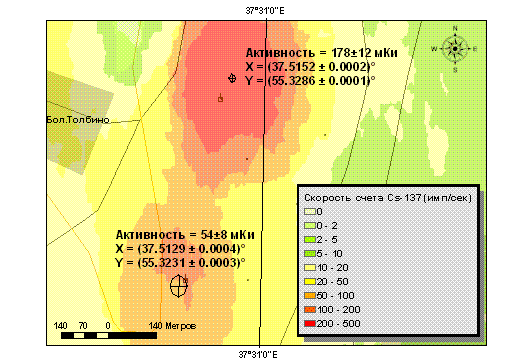
Two Cs-137 sources localization.
|